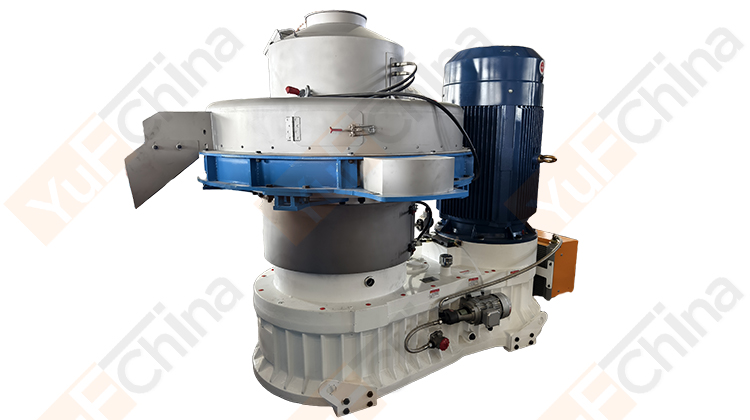
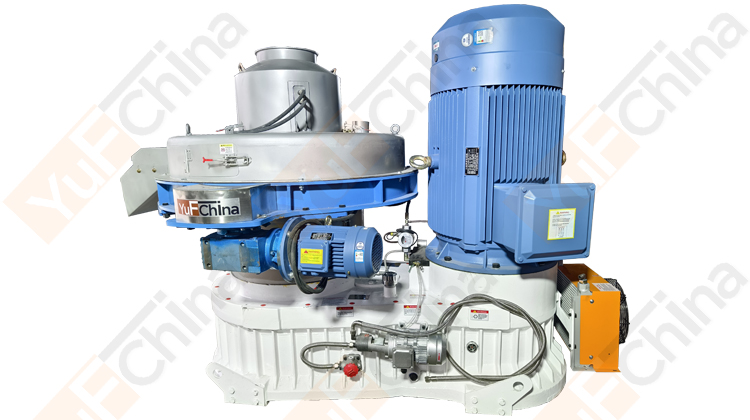
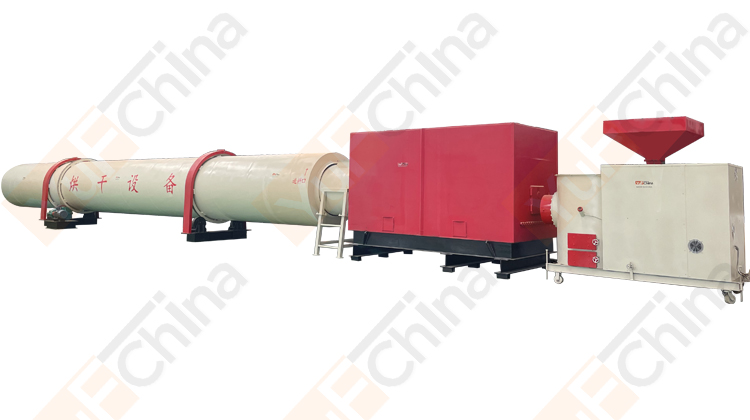
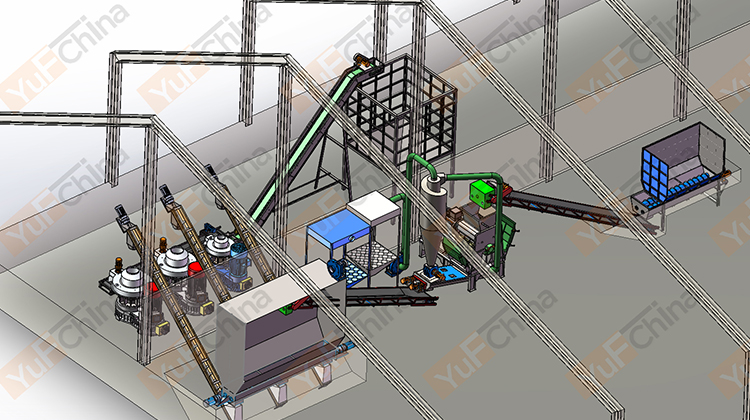
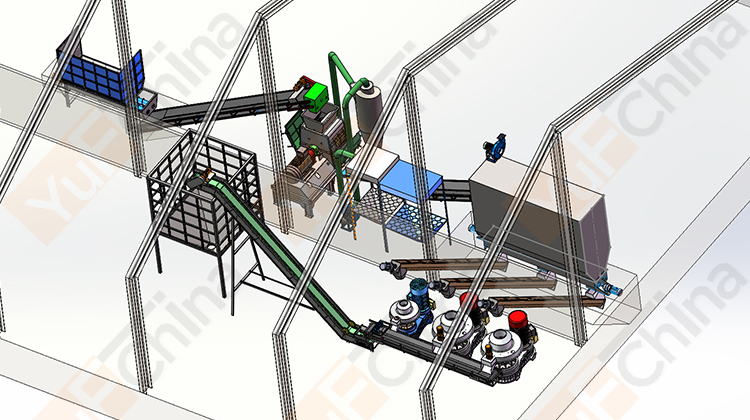
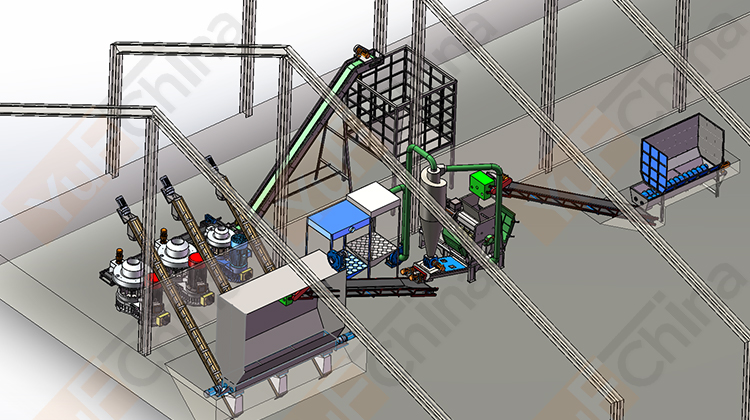
Introduction of Simple cooling Silo
The pellet silo design emphasizes simplicity and ease of use, making it an ideal choice for both small-scale operations and medium-scale industries. The wood pellet storage silo uses natural cooling to make the pellets reach the same temperature as indoors and store them, which is more cost-effective than a cooling machine. Additionally, the natural cooling silo's construction is durable and corrosion-resistant, ensuring long-lasting performance and minimizing maintenance requirements.
Features of Simple Cooling Silo
1. Energy-Efficient: The Natural Cooling Silo utilizes natural cooling processes, significantly reducing energy consumption compared to traditional cooling methods. This not only lowers operational costs but also contributes to environmental sustainability.
2. Temperature Consistency: The advanced cooling technology maintains a consistent temperature throughout the silo, preventing thermal stress and ensuring the pellets remain in optimal condition.
3. User-Friendly Interface: Energy-efficient Storage Silo no control system is needed, eliminating the requirement for manual inspection.
4. Modular Design: The ECO friendly cooling silo's modular construction allows for easy expansion or modification to accommodate growing storage needs or different material types.
5. Cost-Effective: By leveraging natural cooling processes, the Simple cooling Silo offers a cost-effective alternative to mechanical cooling systems. This reduces initial investment costs and ongoing operational expenses.
6. Environmentally Friendly: The use of natural cooling methods minimizes the carbon footprint, aligning with eco-friendly practices and sustainable development goals.
7. Low Maintenance: The durable and corrosion-resistant materials used in the silo's construction ensure minimal maintenance requirements, reducing downtime and maintaining high operational efficiency.
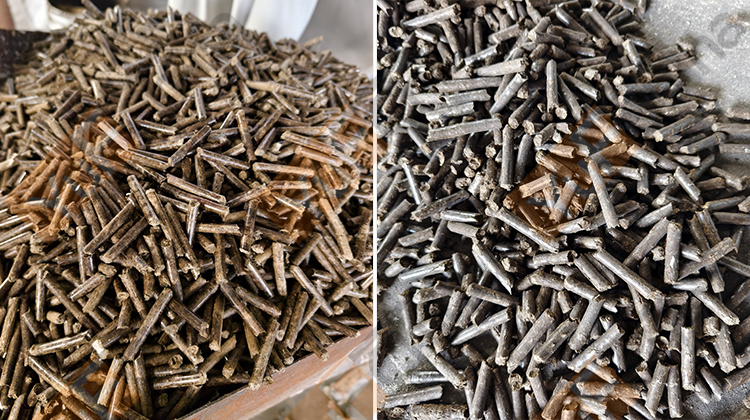
Why do pellets need to be cooled after production?
1. Physical Property Stabilization: When pellets are freshly produced, they are often at an elevated temperature due to the heat generated during the production process, such as extrusion or pelletization. High temperatures can make the pellets soft and malleable. Cooling helps to solidify the pellets, fixing their shape and size. This is crucial for maintaining consistent product dimensions, which is essential for downstream applications.
2. Hygroscopicity Control: Numerous pellet varieties, particularly those derived from agricultural products, exhibit hygroscopic properties, indicating their ability to draw in moisture from their surroundings. Pellets that are hot are more prone to rapid moisture absorption. Cooling the pellets can diminish their rate of moisture uptake. For example, within the feed and biomass sectors, if warm animal feed pellets or fuel pellets absorb excessive moisture, they may become moldy. This not only diminishes the feed's nutritional value but can also pose health risks to the animals ingesting it. Moreover, for fuel pellets, increased moisture content makes ignition more challenging.
3. Safety and Packing: Hot pellets can pose a safety hazard to workers handling them. Cooling the pellets to a safe temperature reduces the risk of burns and other heat - related injuries. In a production facility where operators are responsible for packaging, transporting, or further processing the pellets, working with cool pellets is much safer.













GET IN TOUCH WITH US